Metabolomics in Infectious Disease Research
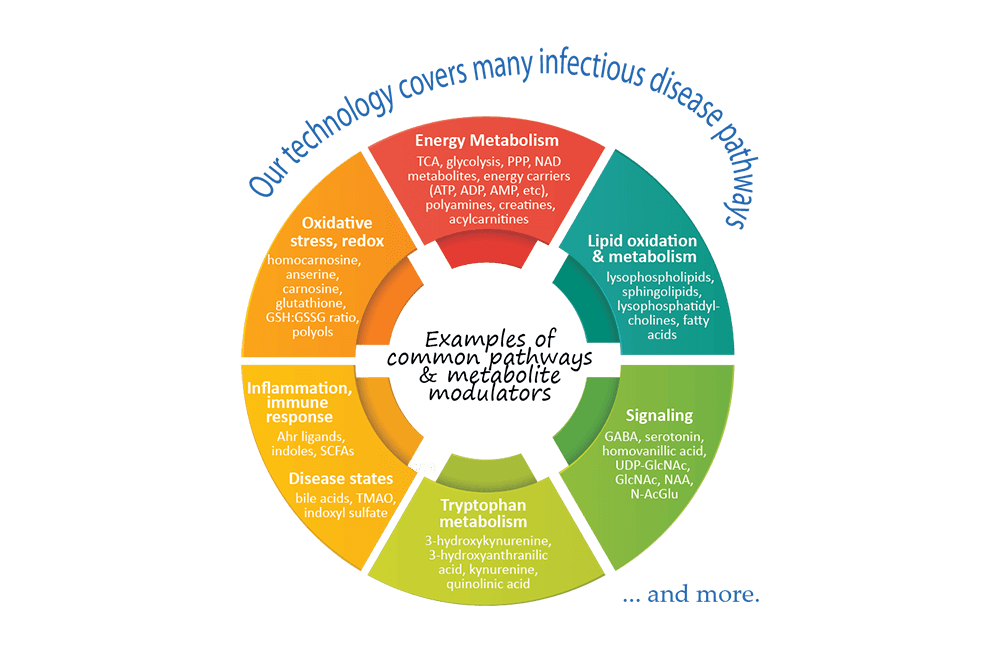
Metabolomics comprehensively characterizes small polar and lipid metabolites, yielding a snapshot of physiological processes that vary according to the pathological state of cells, tissues, and organs. Therefore, the use of metabolomics can help to reveal specific metabolic alterations and potential biomarkers that are associated with disease severity in patients with systemic infections. Furthermore, metabolomics has a great potential for exploring predictive and risk markers of disease development. This will contribute immensely to the treatment and prevention of infectious diseases.